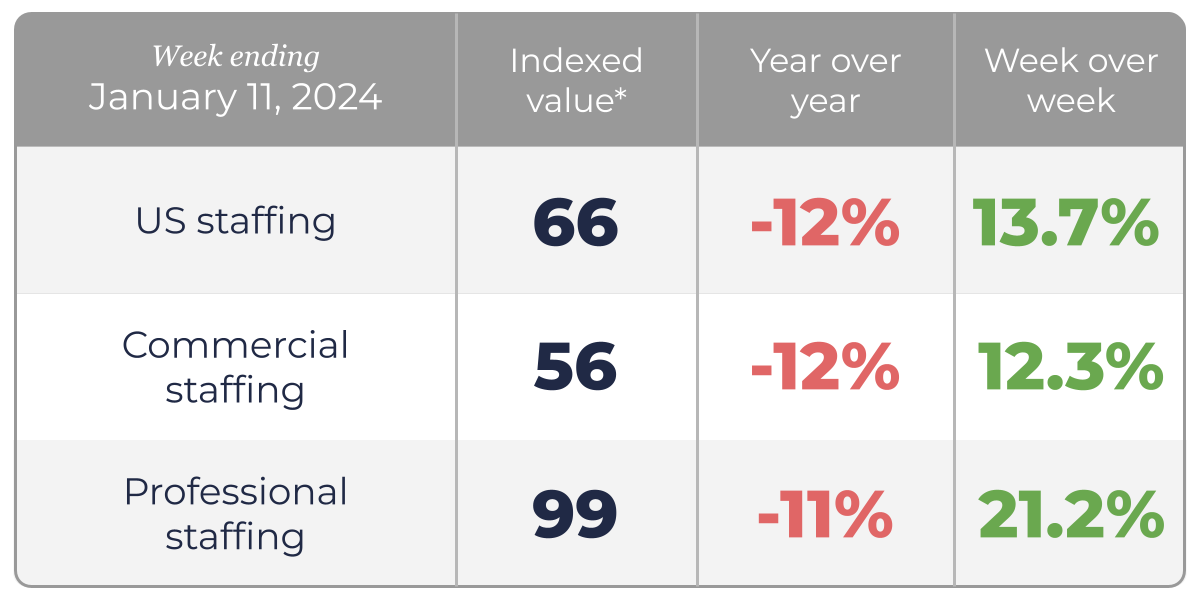
US Staffing hours begin to bounce back after holiday
US staffing hours were up 13.7% compared to the first week of 2025 as businesses reopen after the holiday season. Similarly, commercial staffing hours were up 12.3% and professional hours up even more week over week at 21.2%.
*Indexed value of US staffing hours benchmarked against the week ending January 19, 2019.
Staffing Industry Analysts' perspective
Hours worked in the US staffing industry in the week ending January 11th decreased by -12% year-over-year. Commercial staffing hours were down -12% while Professional staffing hours were down -11%.
The strong sequential increase illustrates how business demand for staffing services typically rebounds in January following holiday season-related closures. We will closely monitor the pace of improvement in the coming weeks.
The US staffing industry is a large and dynamic market that continues to offer big opportunities
The volume of hours remains below last year’s levels. The year-over-year decline in the Indicator is directionally in line with the decline in temporary help employment as reported in the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ monthly Employment Situation reports. The January 2025 US Jobs Report (published on January 10th) estimates that employment in the temporary help services industry declined by -3.8% in December 2024, on a Y/Y basis; and was stable (0.2%) when compared with November 2024.
With the US economy continuing to show a GDP growth rate of more than 2%, and the US elections now behind us, we are keeping our eyes open for signs of an eventual uptick in demand for temporary staffing.
Competitive pressures remain elevated but there are continuing and large opportunities for those staffing firms that have developed a competitive advantage via either their technology, their service offerings, or both. For more discussion of the market dynamics for each skill segment of staffing, SIA Corporate Members are encouraged to read our latest US Staffing Industry Forecast report, published on September 10th. To read more about the current staffing environment, please see SIA’s Insights on the Recent Downturn in US Temporary Staffing 2024 report.
About the SIA Bullhorn Staffing Industry Indicator
The SIA | Bullhorn Staffing Indicator is a unique tool for gauging near real time weekly trends in the volume of temporary staffing delivered by US staffing firms. Each week the Indicator reports data for the week that ended ten days prior to the release. It reflects weekly hours worked by temporary workers across a sample of staffing companies in the US that utilize Bullhorn’s technology solutions. The Indicator is weighted and benchmarked against US Bureau of Labor Statistics data to approximate the composition of the staffing industry by skill. While the indicator does not presume to perfectly reflect the entire universe of US staffing firms, it does represent a sizable sample of the US staffing industry, reflecting a wide range of occupations, client industry verticals, and geographic footprint that spans the country.
The Indicator can be used by staffing firms to benchmark their past and current performance, as well as a tool for forecasting near term industry trends and outlook.
As the US temporary staffing industry has often functioned as a co-incident indicator for the US labor market and economy, the SIA | Bullhorn Staffing Indicator is also useful for a broader audience of business leaders and investors who are seeking real-time insight.
The Indicator is a joint custom research effort between Bullhorn and industry advisor Staffing Industry Analysts.
Revisions and Technical notes on the SIA | Bullhorn Staffing Indicator
We note the readings for the last 4 weeks are subject to revision and so should be viewed as preliminary, with the reading for the last recorded week the most likely to be revised in next week’s data release. For further information on how the Indicator has been created and detailed technical notes please refer to the methodology.









